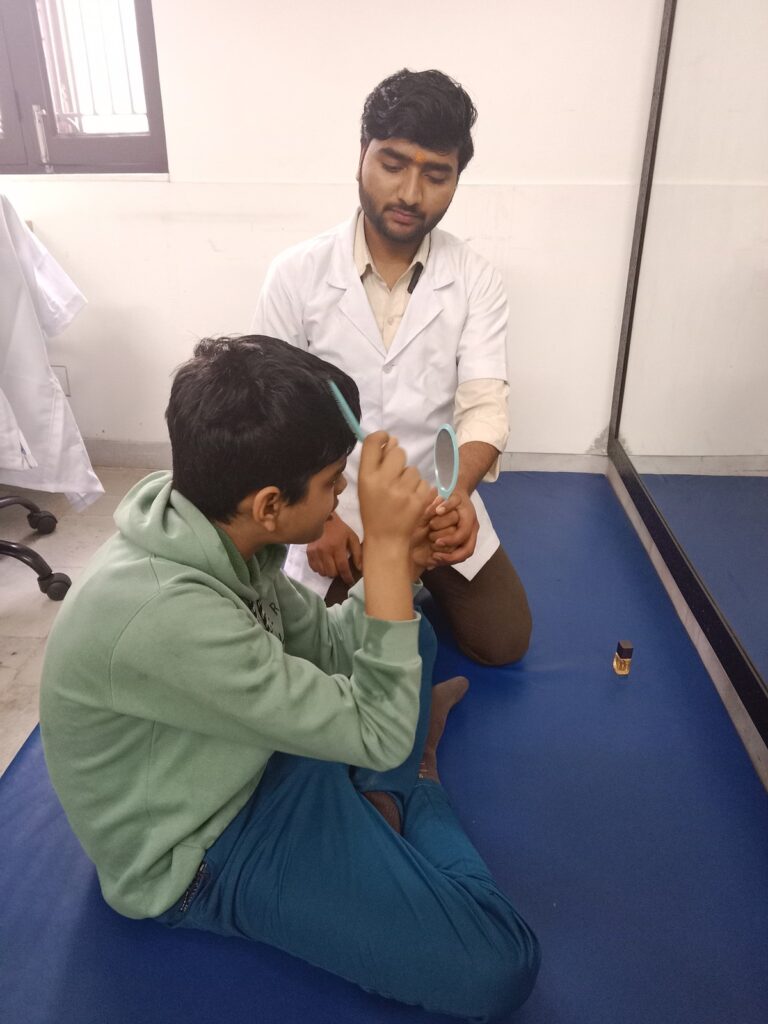
Activities of Daily Living (ADL)
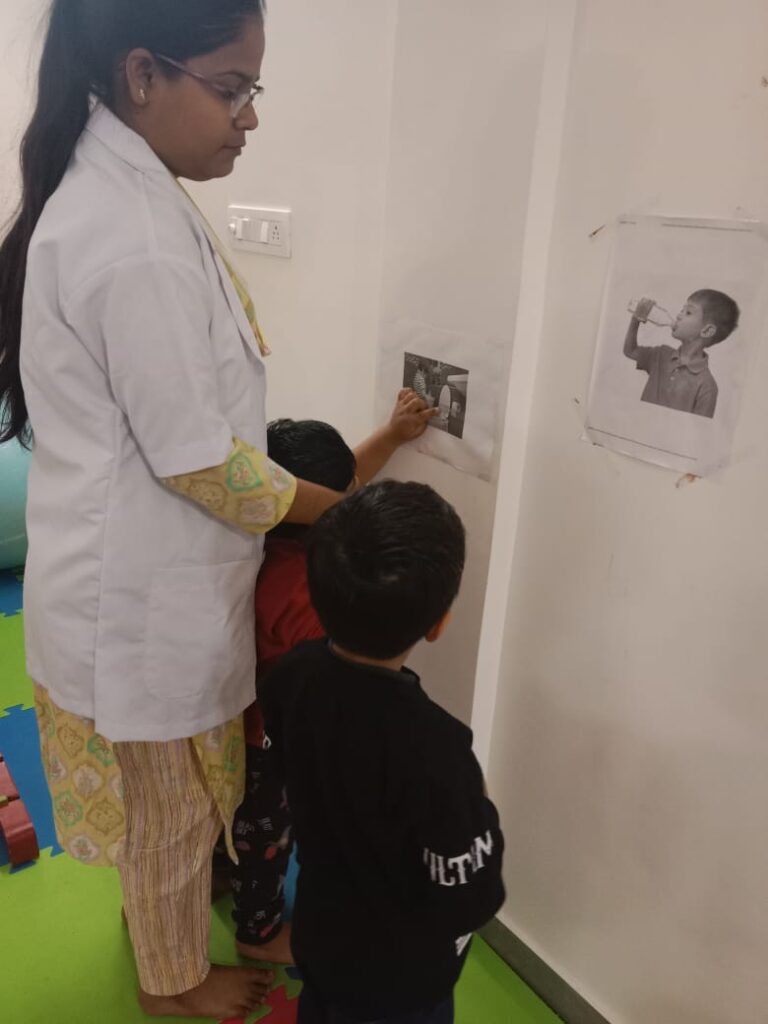
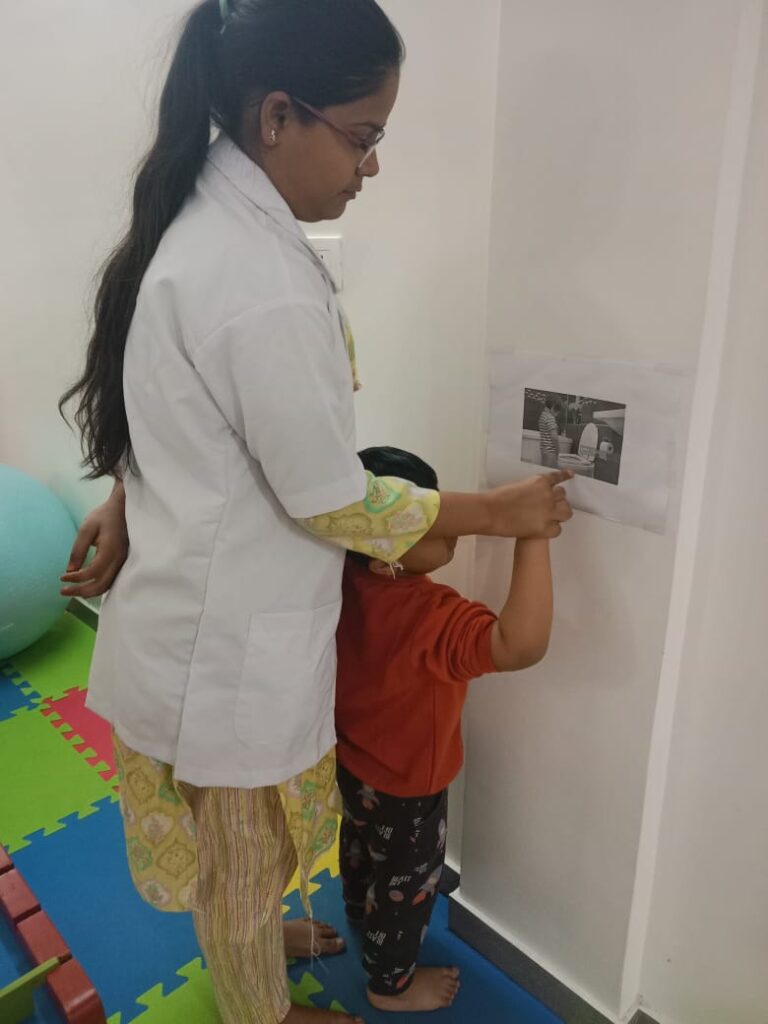
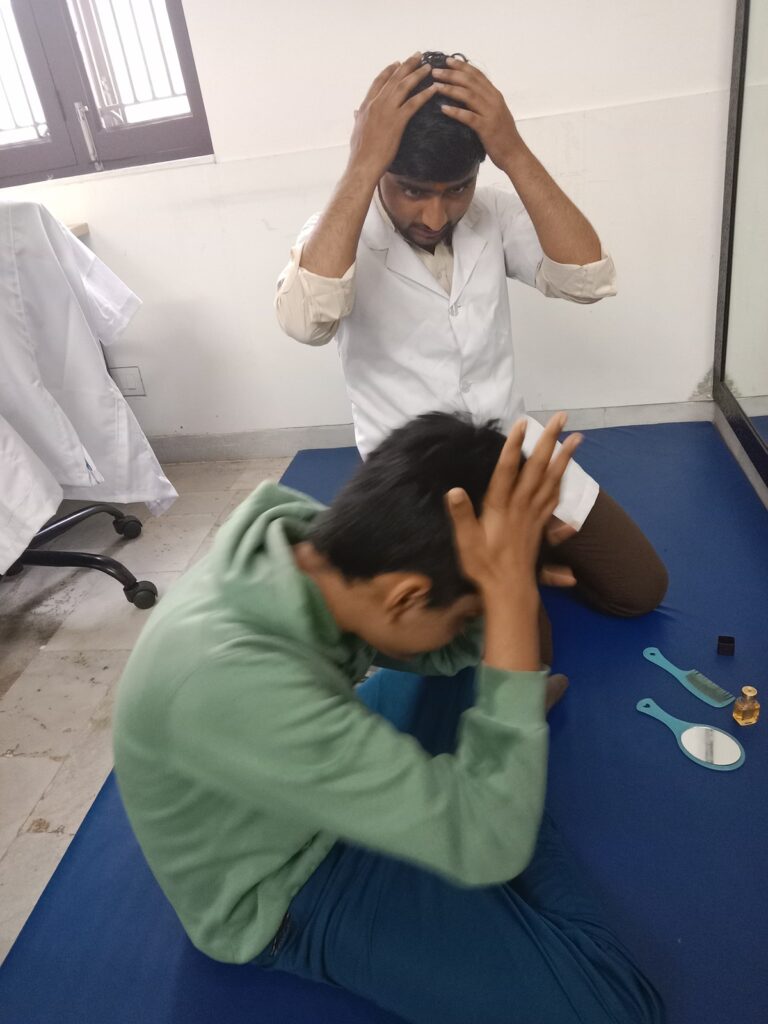
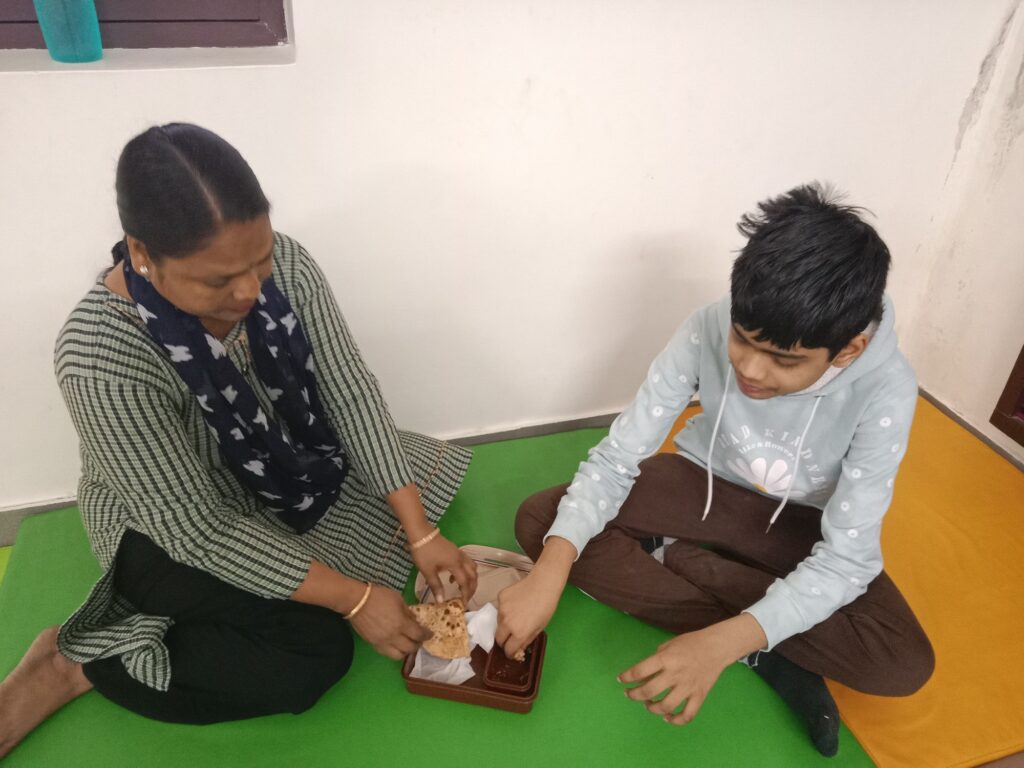
Activities of Daily Living (ADL) therapy is more than just therapy; it’s a gateway to reclaiming one’s life. Whether it’s an elderly individual striving to stay independent at home, a child with disability learning essential skills, or a post-surgery patient regaining functionality, ADL therapy empowers individuals to navigate the daily landscape with confidence and dignity
The therapy is beneficial for individuals facing challenges due to injury, illness, or age-related issues. Whether recovering from surgery or managing a chronic condition, our therapists tailor programs to meet unique needs. This therapy focuses on the essential skills we need to function independently in our daily lives and is a beacon of hope for regaining independence and dignity.
1. Assessment: The therapy begins with a thorough assessment of the individual’s current capabilities, challenges, and goals related to ADLs. This assessment helps identify specific areas of need.
2.Goal Setting: Based on the assessment, clear and achievable goals are established for the individual. These goals could include improvements in dressing, grooming, bathing, cooking, or other ADLs.
3.Individualized Treatment Plan: An individualized treatment plan is developed to target the identified areas of need. The plan may include exercises, activities, and techniques to enhance skills and adapt to limitations.
4.Skill Building: ADL therapy focuses on developing the necessary skills and techniques to perform daily tasks more effectively. This may include exercises to improve strength, coordination, and fine motor skills.
5.Adaptive Strategies: Therapists teach adaptive strategies and provide assistive devices or tools that can help individuals compensate for specific limitations. For example, providing buttonhooks or modified utensils.
6.Practice and Repetition: Regular practice is essential to reinforce newly acquired skills. Individuals work on ADLs within therapy sessions and continue to practice at home.
7.Environmental Modifications: Therapists may suggest modifications to the individual’s home environment to make it more accessible and user-friendly, such as installing grab bars in the bathroom or rearranging furniture.
8.Education and Training: Both the individual and their caregivers or family members may receive education and training to ensure a supportive and consistent approach to ADLs.
9.Progress Monitoring: Progress is regularly monitored and adjustments are made to the treatment plan as needed to help the individual reach their goals.
10.Emotional Support: Therapists provide emotional support and encouragement to individuals as they work toward greater independence in performing ADLs.
ADL therapy can be beneficial for a wide range of individuals, including those with physical disabilities, neurological conditions, aging-related challenges, and those recovering from injuries or surgeries. The ultimate goal is to enhance an individual’s quality of life by promoting independence in daily activities and improving overall well-being.
The therapy is beneficial for individuals facing challenges due to injury, illness, or age-related issues. Whether recovering from surgery or managing a chronic condition, our therapists tailor programs to meet unique needs. This therapy focuses on the essential skills we need to function independently in our daily lives and is a beacon of hope for regaining independence and dignity.
Assessment: The therapy begins with a thorough assessment of the individual’s current capabilities, challenges, and goals related to ADLs. This assessment helps identify specific areas of need.
Goal Setting: Based on the assessment, clear and achievable goals are established for the individual. These goals could include improvements in dressing, grooming, bathing, cooking, or other ADLs.
Individualized Treatment Plan: An individualized treatment plan is developed to target the identified areas of need. The plan may include exercises, activities, and techniques to enhance skills and adapt to limitations.
Skill Building: ADL therapy focuses on developing the necessary skills and techniques to perform daily tasks more effectively. This may include exercises to improve strength, coordination, and fine motor skills.
Adaptive Strategies: Therapists teach adaptive strategies and provide assistive devices or tools that can help individuals compensate for specific limitations. For example, providing buttonhooks or modified utensils.
Practice and Repetition: Regular practice is essential to reinforce newly acquired skills. Individuals work on ADLs within therapy sessions and continue to practice at home.
Environmental Modifications: Therapists may suggest modifications to the individual’s home environment to make it more accessible and user-friendly, such as installing grab bars in the bathroom or rearranging furniture.
Education and Training: Both the individual and their caregivers or family members may receive education and training to ensure a supportive and consistent approach to ADLs.
Progress Monitoring: Progress is regularly monitored and adjustments are made to the treatment plan as needed to help the individual reach their goals.
Emotional Support: Therapists provide emotional support and encouragement to individuals as they work toward greater independence in performing ADLs.
ADL therapy can be beneficial for a wide range of individuals, including those with physical disabilities, neurological conditions, aging-related challenges, and those recovering from injuries or surgeries. The ultimate goal is to enhance an individual’s quality of life by promoting independence in daily activities and improving overall well-being.